Comparative Analysis of All-Ceramic Versus Metal-Ceramic Crowns
Dental crowns are essential for restoring damaged teeth, with two popular types being all-ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns. Understanding the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of these materials helps patients make informed decisions about their dental treatments. This article offers a comparative analysis of all-ceramic cosmetic crowns, focusing on their composition, aesthetics, durability, and clinical performance.
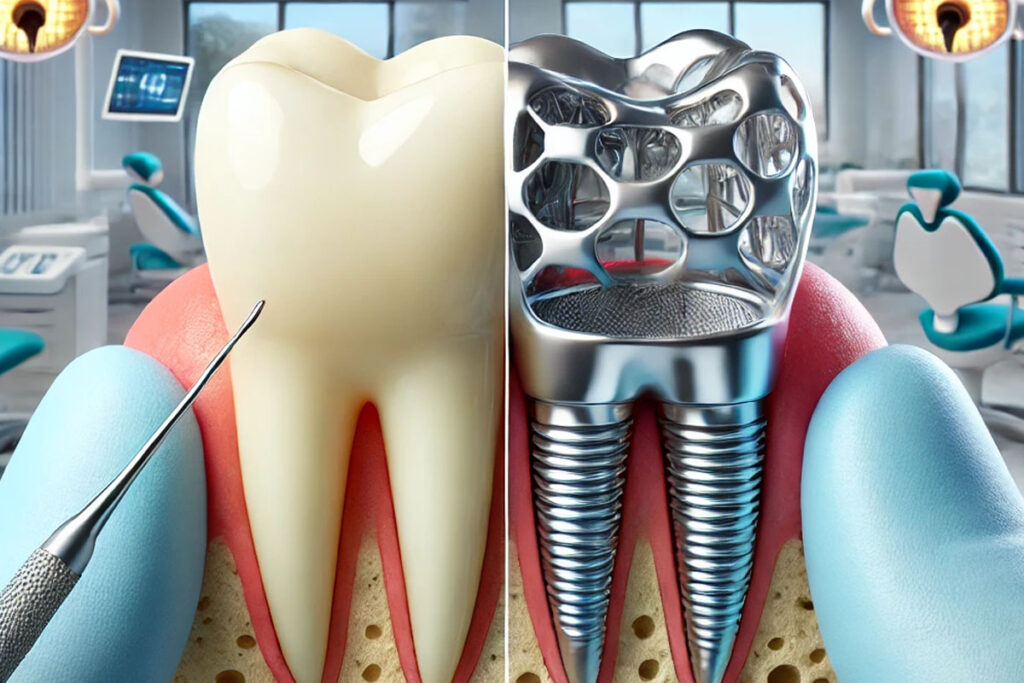
Composition and structure
All-Ceramic Crowns
All-ceramic crowns are made entirely from ceramic materials like porcelain or zirconia. These crowns offer excellent aesthetic qualities, closely mimicking the natural translucency and color of teeth. The absence of metal ensures that light passes through the crown as it would through a natural tooth, providing a more natural look.
Metal-Ceramic Crowns
they, also known as porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns, combine a metal substructure with a ceramic overlay. The metal framework provides strength and support, while the ceramic exterior offers a tooth-like appearance. However, the metal core can sometimes show through the ceramic, especially at the gum line, affecting aesthetics.
Aesthetics
Natural appearance
All-ceramic crowns are preferred for their superior aesthetic appeal. They are ideal for front teeth restorations where appearance is crucial. The ability to match the color and translucency of natural teeth makes them virtually indistinguishable from adjacent teeth.
Limitations
these, while aesthetically pleasing, may not achieve the same level of natural appearance as these. The underlying metal can create a darker appearance at the margins over time, especially if gum recession occurs.
Strength and durability
Durability of All-Ceramic Crowns
Advancements in ceramic materials have significantly improved the strength and durability of all-ceramic crowns. Zirconia crowns, in particular, offer high fracture toughness and resistance to wear. However, they might not be as robust as they in high-stress areas, such as the molars.
Strength of Metal-Ceramic Crowns
The metal framework of PFM crowns provides exceptional strength and durability, making them suitable for both front and back teeth. They can withstand significant biting forces and are less likely to fracture under pressure compared to these.
Biocompatibility and safety
All-Ceramic Crowns
Ceramic materials are biocompatible, meaning they do not cause adverse reactions in the body. This makes all-ceramic crowns an excellent choice for patients with metal allergies or sensitivities. The smooth surface of ceramic also reduces plaque accumulation, promoting better oral health.
Metal-Ceramic Crowns
While generally safe, They may cause allergic reactions in some patients due to this content. The risk of gum irritation and allergic responses can be a concern for individuals with metal sensitivities.
Cost considerations
All-Ceramic Crowns
The cost of all-ceramic crowns is typically higher than these due to the materials and technology involved. However, the investment is often justified by the superior aesthetic results and biocompatibility.
Metal-Ceramic Crowns
PFM crowns are generally more affordable and offer a good balance between strength and appearance. They provide a cost-effective solution to restoring both anterior and posterior teeth.
Conclusion
Choosing between all-ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns depends on various factors, including aesthetics, strength, biocompatibility, and cost. All-ceramic crowns excel in appearance and biocompatibility, making them ideal for visible teeth restorations. these, with their superior strength and durability, are suitable for high-stress areas and offer a balance between cost and performance. Consulting with a dental professional can help determine the best option based on individual needs and preferences, ensuring a successful and satisfying dental restoration.